I’m a huge fan of nootropics, substances which are chemicals that are said to boost brain performance. The issue with the majority of nootropics is that they have no discernible impact. This is known as the “effectiveness problem,” and it is seen in almost all commercially marketed supplements. A supplement, as the name indicates, usually fills a deficiency. Even really beneficial supplements are rarely helpful for those of us who can afford a well-balanced diet. The number of supplements that an individual can benefit from taking on a regular basis is quite limited, and the advantages seldom last beyond replacing the shortage.
Nootropics, a type of food, promise to improve brain function beyond normal, unlike caffeine, which increases alertness by altering the brain’s natural state. Despite research showing otherwise, many believe a raised IQ will lead to happiness and better health.
“Lion’s Mane” is a true nootropic because it permanently enhances cognition by improving the brain’s ability to alter itself structurally.
Let’s find out what’s most important about the Lion’s Mane mushroom .

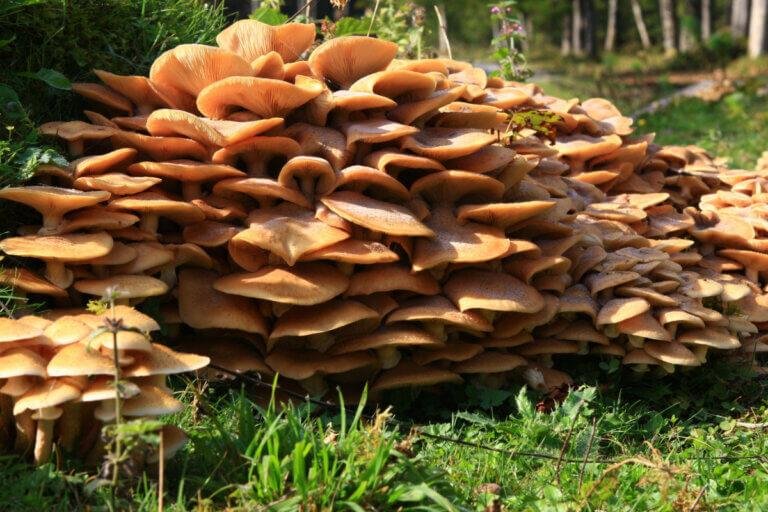
The appearance of the lion's mane mushroom
Lion’s mane mushrooms, scientifically known as Hericium erinaceus, are a unique and fascinating species of fungi. They get their name from their striking resemblance to the mane of a lion, with long, flowing, white tendrils cascading down. But there is so much more to these mushrooms than just their appearance.
History of lion's mane mushroom
Lion’s mane has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for hundreds of years. this fungus has been known to aid the spleen, liver, lungs, kidneys and the heart. During the 1950s, traditional Chinese medicine became a standard practice under the communist and nationalist rule of Mao Zedong. Functional mushrooms, like lion’s mane, reishi, and chaga, are now commonplace in modern medicine in China.
So, Lion’s Mane was foraged from the wild until it was first cultivated in China in 1988 to meet growing demand for the medicinal mushroom. The mushroom has also been used by Buddhist Shaolin monks in Japan over 2,000 years ago, who used lion’s mane in powder form during their meditation practices to improve focus and cognitive function.
As modern science continues to study Lion’s Mane mushrooms, we are discovering even more potential health benefits that align with the traditional uses of this incredible fungus. In the following sections, we will explore these health benefits in more detail and discuss how you can incorporate Lion’s Mane mushrooms into your daily routine for optimal well-being.
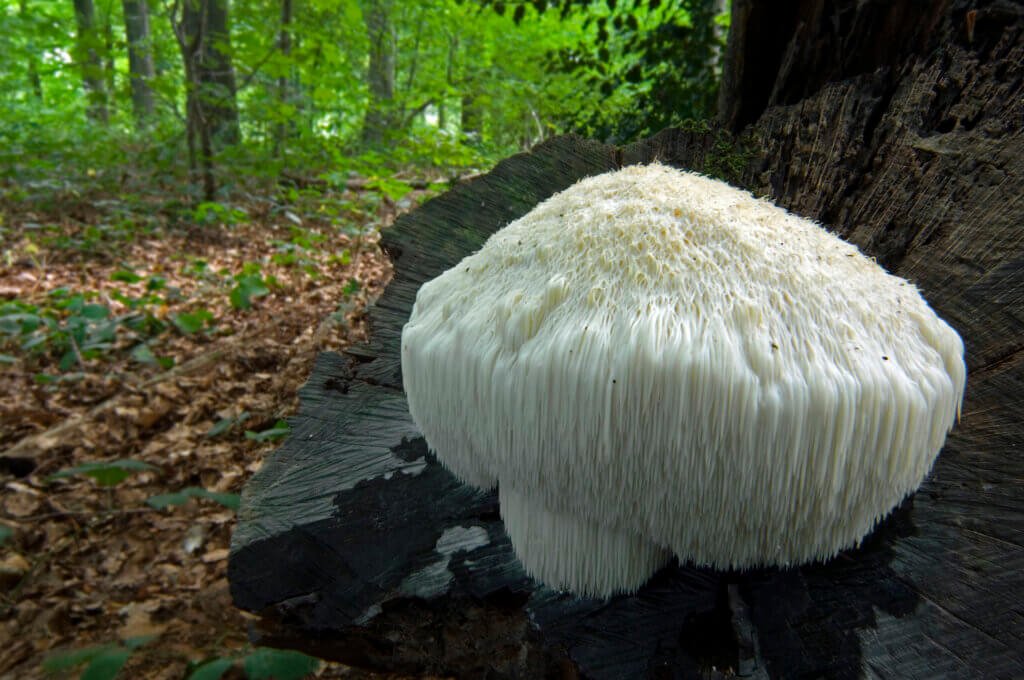

Health benefits of the lion's mane mushroom.
Many therapeutic substances, such as penicillin, were first extracted from fungus.
Fungi create a large number of bioactive chemicals, many of which have yet to be studied for possible medical advantages.
According to a new study, nerve cells exposed to chemicals derived from lion’s mane mushrooms can increase neuron proliferation.
According to a 2015 abstract in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, lion’s mane may help protect nerves from illness or decline. The same study concluded that the mushroom has additional health-promoting properties, such as:
- Regulates blood sugar
- Reduces high blood pressure
- Promotes healthy energy levels and combats fatigue
- Helps to prevent excess blood lipid accumulation
- Protects heart health
- Slows biological aging
- Protects liver health
- Protects kidney health
Enhances brain function
Scientists in South Korea and Australia examined how fungi influence neurons in the laboratory. They did this by separating crude extracts of lion’s mane fungi and testing them on neurons.
They published their findings in the Journal of Neurochemistry.
CNGBio Co, which grows organic mushrooms for therapeutic uses, supported the study.
So much so that it has gained the title “the smart mushroom” due to its potential to boost cognitive function and minimize brain fog.
Nerve growth factor (NGF) production: Lion’s Mane contains compounds called hericenones and erinacines, which have been found to stimulate the production of NGF in the brain. NGF is a protein that promotes the growth, maintenance, and survival of nerve cells, thus enhancing brain function. It also plays a crucial role in neuroplasticity, learning, and memory.
Reduced Symptoms of Cognitive Decline: Certain studies suggest that Lion’s Mane may have potential benefits in addressing cognitive decline associated with conditions like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. The bioactive compounds in Lion’s Mane may promote the production of growth factors and protect against brain damage, ultimately improving cognitive function.
Supports nervous system health
Reduced inflammation and oxidative stress: Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress can have a negative impact on brain health and cognitive function. Lion’s Mane contains antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compounds that can help reduce inflammation and oxidative stress in the brain, thus protecting brain cells and enhancing cognitive function.
Potential neuroprotective effects: Lion’s Mane has been studied for its potential neuroprotective effects. It may help protect the brain against age-related cognitive decline, neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, and other neurological disorders. Some studies have shown that Lion’s Mane can help reduce the accumulation of beta-amyloid plaques in the brain, which are associated with Alzheimer’s disease.

Potential alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression
One study published in 2018 investigated the effects of Lion’s Mane on depressive behaviors in mice. The researchers found that Lion’s Mane supplementation reduced symptoms of depression by modulating the levels of certain neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine.
Another study in 2010 examined the effects of Lion’s Mane on menopausal women with anxiety and depression symptoms. After consuming Lion’s Mane extract for four weeks, the participants reported a reduction in anxiety and irritation, as well as an improvement in sleep quality.
Although these studies indicate potential benefits, it is important to note that the research on Lion’s Mane and mental health is still in its early stages. More studies and clinical trials are needed to fully understand the mechanisms and efficacy of Lion’s Mane for anxiety and depression treatment.

Boosts immune system
Research has indicated that Lion’s Mane may have the ability to:
Boost immune cell activity: Studies have found that Lion’s Mane can increase the production and activity of various immune cells, including natural killer (NK) cells, which play a crucial role in fighting off infections and tumors.
Enhance the production of cytokines: Cytokines are signaling molecules that coordinate immune responses. Lion’s Mane has been found to stimulate the production of certain cytokines, such as interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), which are involved in inflammation and immune defense.
Supports digestive health
Anti-inflammatory effects: Lion’s mane mushrooms contain compounds, such as polysaccharides, that have anti-inflammatory properties. Inflammation in the digestive system can lead to conditions like gastritis or inflammatory bowel disease. The anti-inflammatory effects of lion’s mane mushrooms can help reduce inflammation and promote overall digestive health.
Promotes gut health: Lion’s mane mushrooms are rich in dietary fiber, which is essential for maintaining a healthy digestive system. Dietary fiber promotes regular bowel movements, prevents constipation, and helps maintain a healthy gut microbiota. A healthy gut microbiota is crucial for proper digestion, nutrient absorption, and immune function.
Supports gastrointestinal mucosa: The consumption of lion’s mane mushrooms may help support the health of the gastrointestinal mucosa. Compounds found in lion’s mane mushrooms, like hericenones and erinacines, have been shown to promote the growth and repair of the mucosal lining in the gastrointestinal tract. This can help protect the digestive system from damage and improve overall gut health.
Provides antioxidant activity
Lion’s mane mushrooms provide antioxidant activity through the presence of bioactive compounds such as phenolic compounds and polysaccharides.
Phenolic compounds: Lion’s mane mushrooms contain various phenolic compounds such as erinacines, hericenones, and benzaldehydes. These compounds have shown potent antioxidant properties and can scavenge free radicals in the body, thereby reducing oxidative stress. They can also inhibit lipid peroxidation, which is the process that damages cell membranes and causes oxidative damage.
Polysaccharides: Lion’s mane mushrooms are rich in polysaccharides, particularly beta-glucans. These polysaccharides have been found to possess antioxidant activity by scavenging free radicals and inhibiting oxidative damage. They can also enhance the activity of antioxidant enzymes in the body, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx), which further help in reducing oxidative stress.
Spiritual benefits of Lion’s Mane

Deepened spiritual connection: Lion’s Mane is believed to enhance spiritual experiences and promote a deeper connection with oneself and the world. It is known for its ability to increase feelings of connectedness, mindfulness, and presence.
Improved clarity and insight: Lion’s Mane has been associated with enhancing clarity, insight, and spiritual growth. It helps in quieting the mind, reducing mental chatter, and gaining a deeper understanding of oneself and the universe.
Increased energy and vitality: Lion’s Mane is known for its adaptogenic properties, which means it helps the body adapt to stress and maintain balance. It can increase energy levels, reduce fatigue, and increase overall vitality, which can benefit spiritual practices and meditation.
Heightened perception and spiritual vision: Lion’s Mane is believed to sharpen the senses, including perception and spiritual vision. It is considered a powerful tool for those practicing divination, energy work, and other spiritual practices.
Emotional healing and transformation: Lion’s Mane can support emotional healing and transformation by promoting neural regeneration and reducing inflammation in the brain. It helps in releasing past traumas, resolving emotional blocks, and fostering personal growth.
Nutrition in lion's mane mushrooms.
Lion’s mane mushrooms, have various nutritional benefits. They are low in calories, fat-free, and contain a good amount of fiber, protein, and carbohydrates. They are also a good source of essential minerals such as potassium, zinc, iron, and selenium. Here is a breakdown of their nutritional composition per 100 grams of lion’s mane mushrooms:
- Calories: 22 kcal
- Protein: 3 grams
- Carbohydrates: 3 grams
- Fiber: 1 gram
- Fat: 0 grams
- Vitamin D: 0 micrograms
- Vitamin C: 3 milligrams
- Calcium: 2 milligrams
- Iron: 0.3 milligrams
- Potassium: 270 milligrams
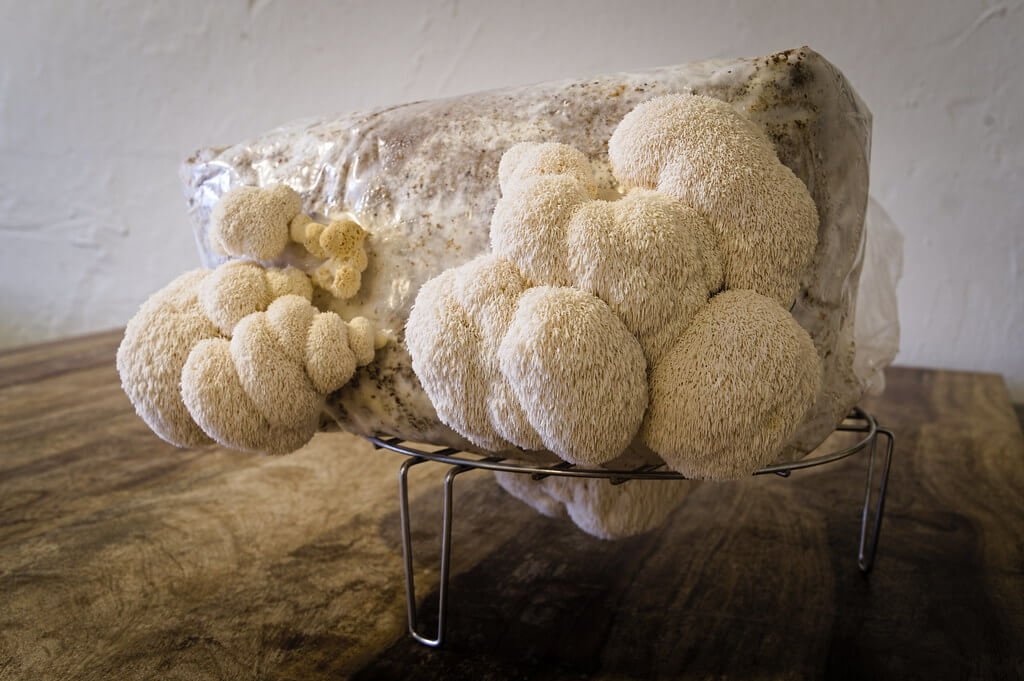

Lion’s mane mushrooms are also a good source of various bioactive compounds and antioxidants, such as polysaccharides, hericenones, and erinacines, which have been studied for their potential health benefits, including immune support and brain health.
Lion's mane mushroom cooking tips.
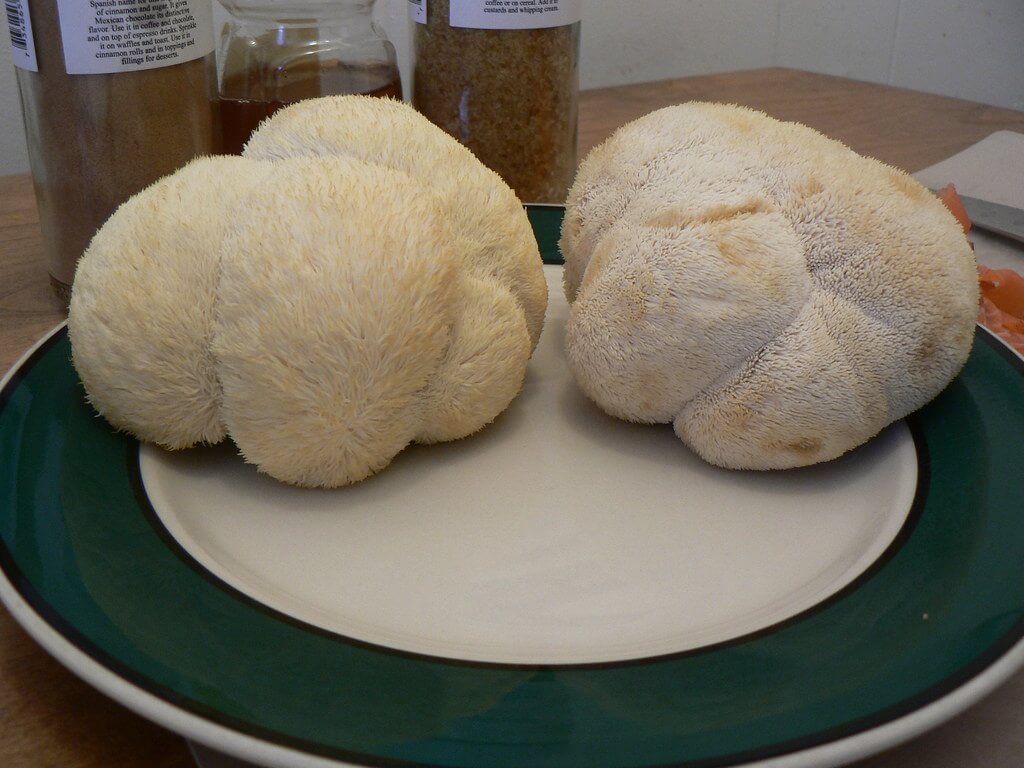

Lion’s mane mushrooms, are a unique culinary ingredient with a meaty texture and a delicate, seafood-like flavor. They are highly versatile and can be used in various culinary applications. Here are some popular culinary uses of lion’s mane mushrooms:
Sautéed or Stir-Fried: Lion’s mane mushrooms can be sautéed or stir-fried in butter or olive oil to bring out their natural flavor and create a tender, meaty texture. They can be seasoned with herbs, garlic, and spices to enhance their taste.
Grilled or Roasted: Grilling or roasting the lion’s mane mushrooms can give them a smoky and slightly charred flavor. Coat them with olive oil, salt, and pepper before placing them on the grill or in the oven.
Substitute for Seafood: Due to their delicate seafood-like flavor, lion’s mane mushrooms can be used as a vegan or vegetarian substitute for seafood in various dishes. They can be used to make vegan scallops, crab cakes, or even lobster-like dishes.
Soup or Stock: Lion’s mane mushrooms can be added to soups, stews, or broths to enrich the flavor and add a meaty texture. They can be sliced or chopped and added to the recipe like any other mushroom.
Pasta or Risotto: Lion’s mane mushrooms can be sliced and added to pasta dishes or risottos. They add a unique texture and flavor to the dish. For best results, sauté them separately before adding them to the pasta or risotto.
Mushroom Tacos or Burgers: Lion’s mane mushrooms can be breaded and fried to create a crispy texture, making them a great filling for tacos or patties for burgers. They can be seasoned with spices and herbs to enhance the taste.
Tempura or Fritters: Dip lion’s mane mushroom slices in a batter and fry them until crispy to create delicious tempura or fritters. They can be served as an appetizer or a side dish.