Why do some people get food when others don’t?
Food Insecurity is a situation where people have access to adequate, safe and nutritious food to maintain a healthy life. Food is a vital necessity for life, but not everyone gets enough of it.
Today, the world faces major food security challenges, and about 2 billion people worldwide suffer from food insecurity, according to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations’s 2020 report. 1.03 billion of these people live in Asia, 675 million in Africa, 205 million in Latin America and the Caribbean, 88 million in North America and Europe, and 5.9 million in Oceania. The number of malnourished people in the world is expected to exceed 840 million by 2030, with factors causing food insecurity, such as poverty, population growth, climate change, urbanization and poor agricultural practices.

How capable are mushrooms to achieve food security?
Mushroom farming can play an important role in supporting food security, and since mushroom farming does not require access to land, it is a viable and attractive activity for both rural farmers and urban dwellers.
Here are 5 main ways in which mushrooms can ensure food security:
Mushrooms help improve soil for agriculture:
In this context, fungi play a crucial role in meeting the needs of food scarcity by supporting its production and insurance. They contain valuable food compounds, such as amino acids, proteins, fibres, vitamins and minerals.
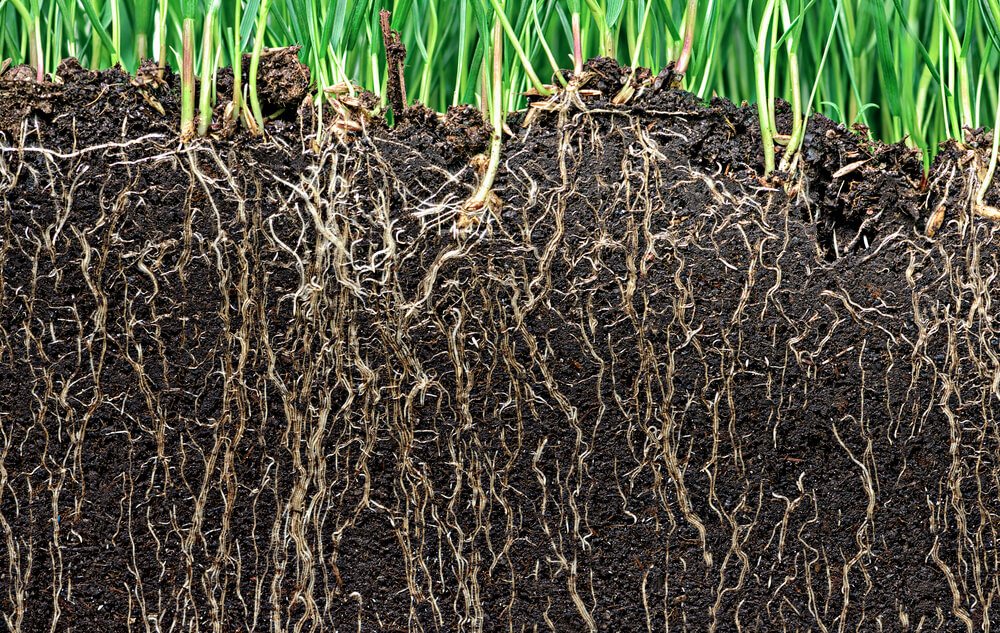

In addition, The Mycorrhizae network contribute significantly to improving nutrition quality and crop health in general, thereby increasing crop productivity. According to a study published in “Nature” the Journal of 2017, Mycorrhizae can significantly improve soil quality.
The Mycorrhizae network connects to the roots of 90 to 95% of the world’s plants, where it helps them acquire nutrients whose roots cannot naturally get them. These fungi can make organic matter usable by crumbling them and converting them to nutrients especially phosphorus.
additionally, mushrooms are used as a natural fertilizer to grow the crop. It is added to the soil after it is used as a food to produce mushrooms. This substance is called fertilizer.
Mushroom as a valuable resource for animal nutrition:

Mushroom waste is the remaining substrate after the cultivation of mushrooms, which contains residual mushroom mycelium and nutrients.
Mushroom waste can be used as an additive or supplement to animal feed, as it is rich in protein, vitamins, minerals, and enzymes.
Mushroom waste can improve the health and performance of farm animals, such as chickens, fish, lambs and livestock, by promoting their digestion, immunity and disease resistance.
Mushroom waste can also transfer some of the medical properties of fungi to animal products, such as eggs, meat and milk, which may have potential benefits for human health.
Mushroom waste can improve the quality and quantity of milk production in milk cows by increasing their intake of dry matter and producing milk, fat and protein in milk.
Mushroom waste can also reduce the environmental impact of mushroom cultivation and animal production by recycling organic materials and reducing waste disposal.
Mushroom waste can also reduce methane emissions by changing livestock feed fermentation.
Mushroom waste can also be used as a substrate to grow other mushrooms or microbes, such as yeast, bacteria or algae
mushrooms contains a good amount of nutrients:
Mushrooms contain many important nutrients for the body, where they contain proteins, vitamins, fats, carbohydrates, amino acids, and minerals.
The value of protein in mushrooms is equal to twice the value of protein in potatoes and cabbage, four times the value of protein in tomatoes and carrots, and six times the value of protein in oranges.
The roast contains various B vitamins, including pantothenic acid (B5), niacin (B3), riboflavin (B2), as well as copper and selenium.
It also contains protein, fibre, potassium, vitamin D and calcium, with a water rate of up to 90%.
Studies suggest that eating 10g of mushrooms a day may provide your body with 125% of its “vitamin D” needs, which is essential for bone health and immune function.


Substitute for medicine:

Mushrooms can be a good alternative to food crops used for medical purposes in sub-Saharan Africa and Asia.
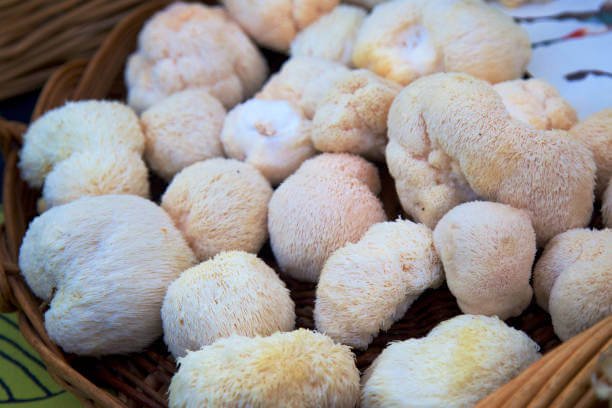

Mushrooms and medical fungi are believed to contain approximately 130 medical functions, including antioxidant, radical scraping, cardiovascular, protective properties of the liver, and resistant to diabetes.
mushrooms contain antibodies and anti-cancer agents that can be used for treatment, as people have done for thousands of years.
Mushrooms are also considered as a good dietary alternative for patients with diabetes or anemia because their carbohydrate levels are very low and contain a high percentage of folic acid.
In addition, mushrooms may do more for your health than energy your body. It contains antibacterial, antiviral, anti-parasitic, antifungal, detoxification and can help reduce cholesterol.
It is good for the immune system because it may help prevent or treat Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, high blood pressure, and cancer.
There are many kinds of medical mushrooms such as Lion’s mane mushrooms, reishi mushrooms, chaga mushrooms, turkey tail mushrooms, shitake mushrooms, and maytake mushrooms. Each type has its own distinctive health benefits.
Other studies suggest that some compounds found in mushrooms may help stimulate nerve growth factor generation (NGF) in nerve cells, which may improve brain and memory function.
Mushroom can be grown easily :
It does not need soil or seeds to grow, but instead it needs spores and organic materials.
Mushroom can be grown indoor or outdoor, in different climates and classes, if there is sufficient moisture and ventilation.
Mushrooms can be grown on various types of waste materials, such as straw, sawdust, or agricultural products, which can reduce environmental pollution and save costs.
Mushrooms can be harvested within weeks after injecting the substrate, a mixture of spores and nutrients.

Mushrooms can be grown using different methods, such as the use of bags, bottles, or trunks, depending on the type of mushrooms and the space available.
Mushrooms can be grown using different techniques, such as sterilization, pasteurization or fermentation, to prevent pollution and promote colonization.
Mushrooms can be grown using different stages, such as composting, pollination, coverage, stabilization and harvesting, to improve the growth and productivity of the mushrooms.

So, now that you know a major way to solve the global food insecurity problem, what do you want to do?
Fungi can be a big part of the solution to the world’s food security problem. With increased awareness and capacity-building on the benefits of fungi in different states and countries, these fungi will become more commercial. Gardeners, gardeners and farmers can benefit from the production and use of fungi in a sustainable way